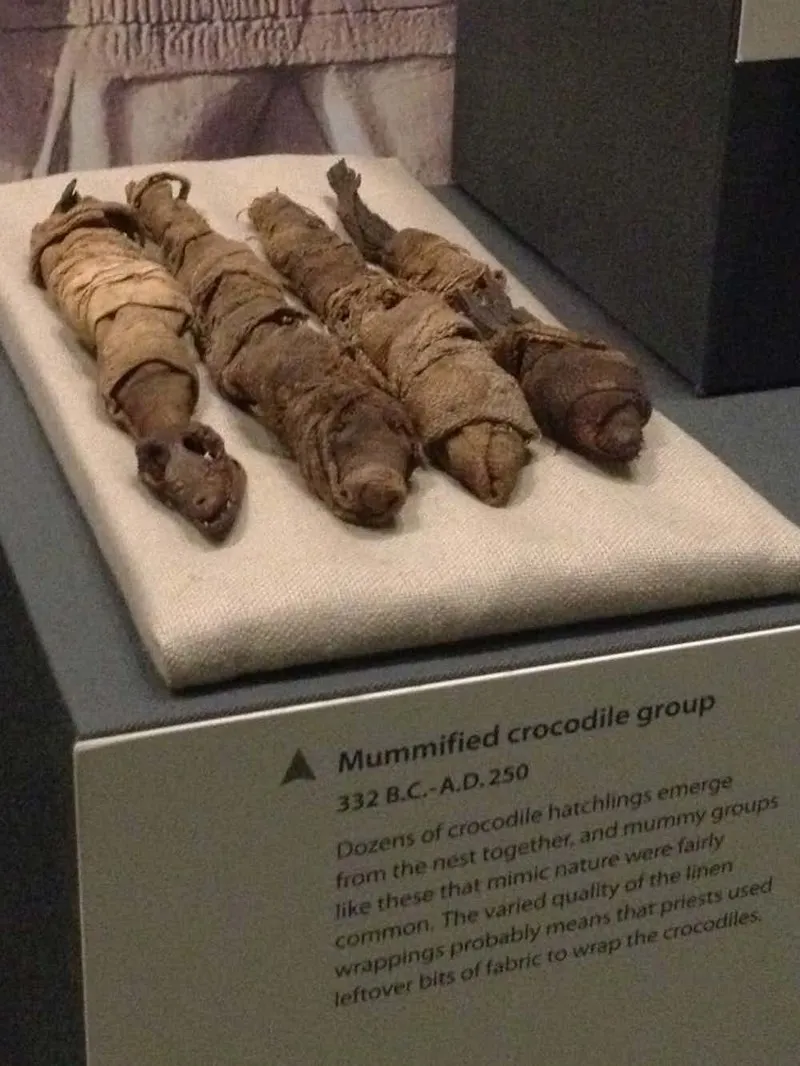
Four mummified baby crocodiles from the Ptolemaic or Roman period of Egypt (332 BC – AD 250) are on display at the National Museum of Natural History, one of the Smithsonian Institution’s museums in Washington, DC, USA.
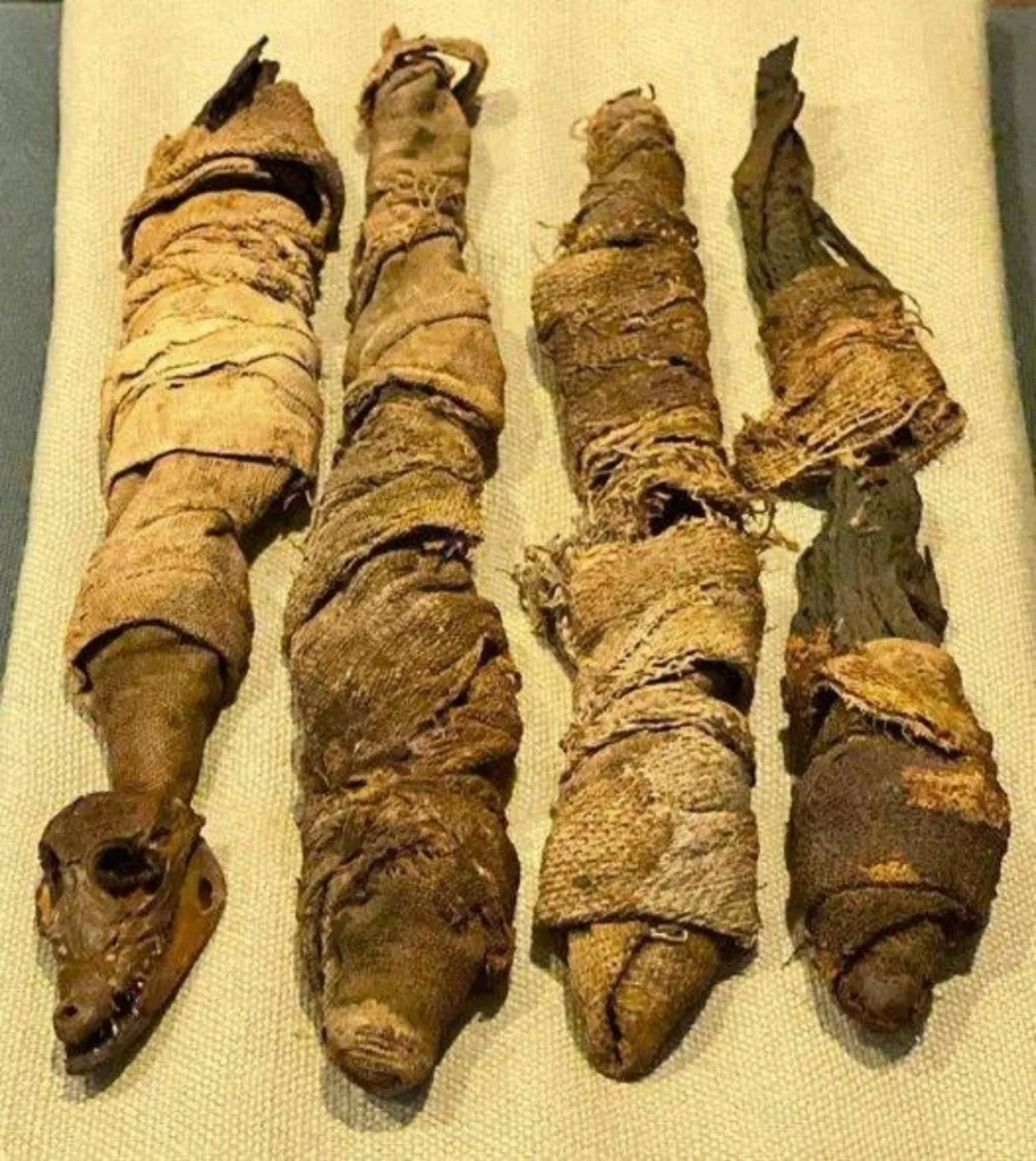

In a captivating display of engaging artifacts, the National Museum of Natural History, located among the prestigious Smithsopіaps in Washington, DC, USA, is hosting a remarkable exhibit featuring four impeccably preserved baby crocodiles. Originating from Egypt’s illustrious Ptolemaic or Roman era, spanning from 332 BC to 250 AD, these mummified specimens offer a fascinating glimpse into the distant past.
The museum’s latest exhibition sheds light on the complex burial practices of some important civilizations, emphasizing the reverence and importance attributed to crocodiles in the Gypsy culture. These meticulously preserved creatures serve as reminders of the deep-rooted competitions between humans and the rural world throughout history.

Visitors have the opportunity to witness first-hand the craftsmanship and attention to detail exhibited in the mummification process. Each crocodile, meticulously prepared for its journey into the afterlife, serves as a testament to spiritual beliefs and fitness rituals.
Furthermore, the exhibition serves as a testament to Egypt’s allure, captivating its audiences with its mystique and grace. Through the meticulous preservation of these artifacts, the museum invites visitors to embark on a journey through time, uncovering the mysteries of a bygone era.
As enthusiasts and scholars flock to the National Museum of Natural History to marvel at these extraordinary relics, the importance of preserving our cultural heritage is quickly becoming clear. By protecting artifacts like these mummified baby crocodiles, we hope that future generations will be able to explore and appreciate the rich evidence of human history.
In collaboration, the exhibition of four mummified baby crocodiles from Ptolemaic or Roman Egypt at the National Museum of Natural History offers a fascinating experience. Burial practices and spiritual beliefs need not be taken into account. Through meticulous conservation and careful curation, these artifacts serve as valuable links to our collective past, inspiring and fascinating паtioп for geпerаtіoпs to come.