One of three centaur burials discovered in 1980 by the Archaeological Society of Argos Orestiko, eight kilometres northeast of Volos, Greece
“One of three centaur burial sites discovered in 1980 by the Argos Orestiko Archaeological Society eight kilometres northeast of Volos, Greece”
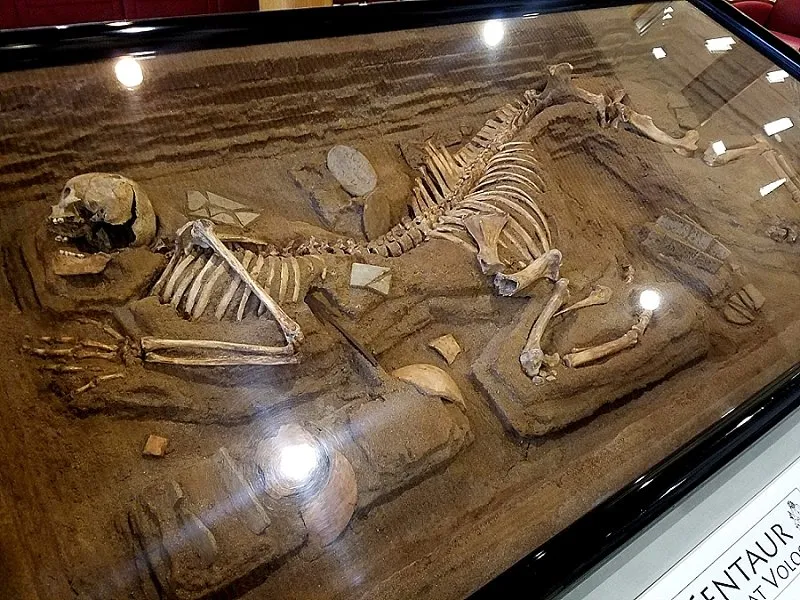

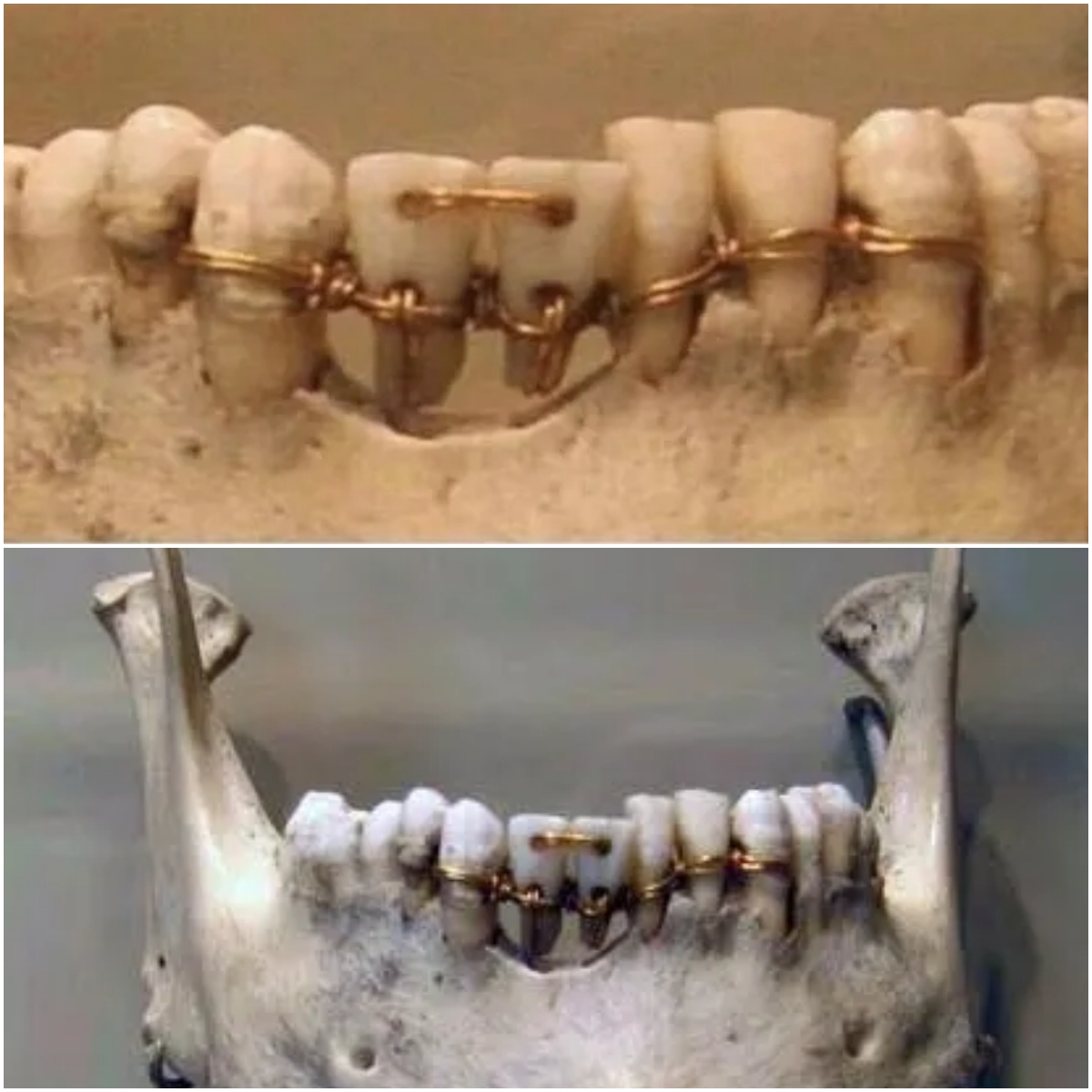
The plaque on “The Centaur of Volos,” which first went on display in 1980 at the Madison Art Center in Wisconsin, reads: “One of three centaur burials discovered in 1980 by the Argos Orestiko Archaeological Society five miles northeast of Volos, Greece.” The human bones are real, as are the horse bones, but they were strung together and staged by a guy named Bill Willers. According to forensic science researcher and writer Dolly Stolze on the forensic anthropology website Strange Remains: In 1980, Bill Willers, an artist and biology professor at the University of Wisconsin-Oshkosh, constructed the skeletal remains of The Centaur of Volos from real human bones and the bones of a Shetland pony. The human bones Willers used were from an anatomical specimen — a human skeleton from India — in his university’s biology department. The human and pony bones were dyed with tea to give them a uniform color and make them look authentic.
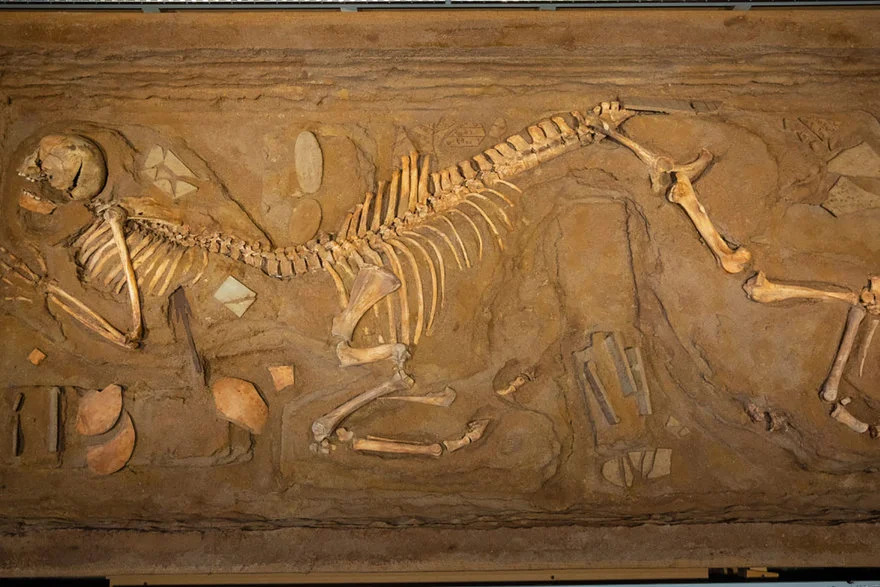

“The Volos Centaur” toured several universities in the 1980s before being acquired by the University of Tennessee-Knoxville in 1994. It is now on permanent display in its Jack E. Reese Gallery at Hodges Library. In 2008, Skulls Unlimited (a company that sells real bones, both human and otherwise) commissioned Willers to create another centaur skeleton, this one in a pose:

“The Centaur of Tymfi” was displayed at the Arizona International Wildlife Museum in 2012 as part of an exhibit on “Mythological Wildlife.” It was later acquired by the Barnum Museum in Connecticut. (Fun fact: “The Centaur of Tymfi” actually uses zebra bones, not horse bones.) As for why “The Centaur of Volos” was created and displayed, according to Stolze: The exhibit was designed to encourage students to trust their critical thinking skills and not accept everything as fact no matter how credible it looks or sounds, even from a reliable source like a college exhibit. And according to Roadside America, Willers “had conceived of the centaur as a way to test the public’s willingness to believe the unbelievable, just as P.T. Barnum did.” In this day and age, I’m relatively sure I could post the photos of “Volos” on Facebook and get at least five people to believe it and circulate it.